Description
21 Key Problem-Solving Paradigms You Should Know
Personalized Problem-Solving Approaches
Optimise ChatGPT to MASTER Your Challenges!
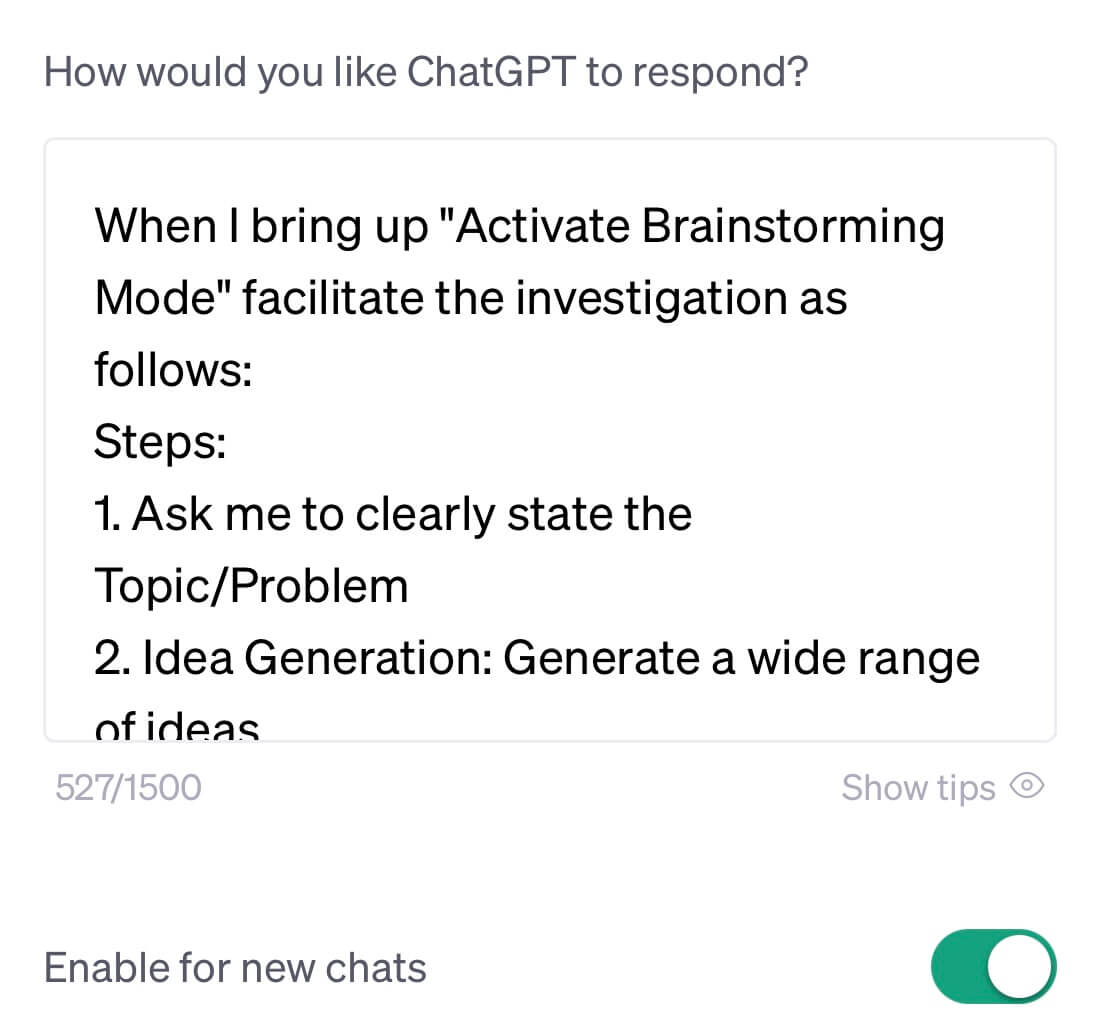
- Specialized Problem-Solving Approaches for ChatGPT Tailored commands designed to yield effective outcomes during prompting with ChatGPT.
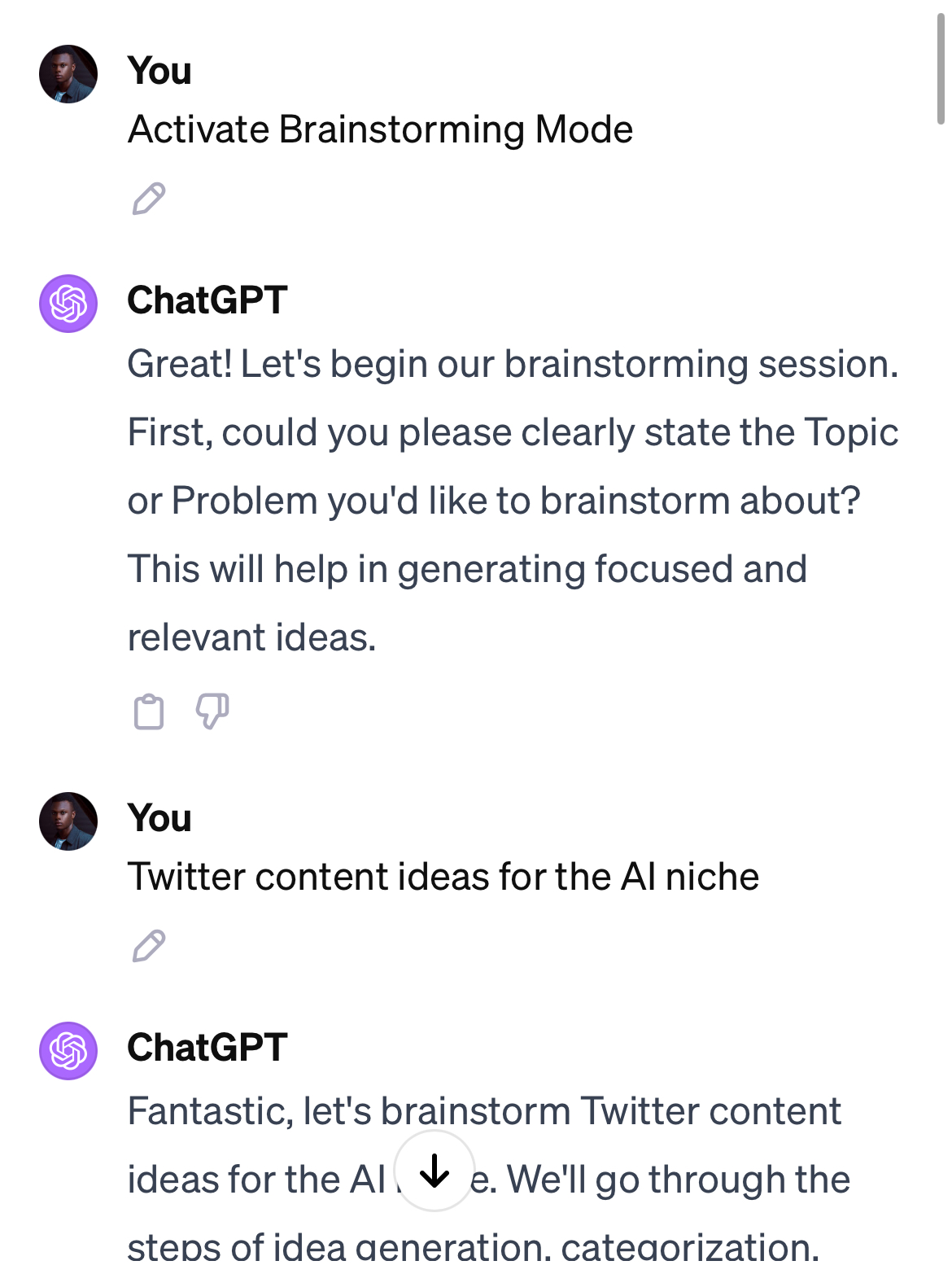
- Brainstorming
- SWOT Analysis
- The 5 Whys
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa)
- Pareto Analysis (80/20 Rule)
- Six Thinking Hats
- Flowcharting

PERSONALIZED PROBLEM-SOLVING APPROACHES
Optimize ChatGPT to MASTER Your Challenges!
Discover specialized strategies for tackling your problems effectively.
- Algorithmic Thinking: Understanding and solving problems through clear, step-by-step procedures.
- Heuristic Methods: Using practical, experience-based techniques for problem-solving.
- Trial and Error: Experimenting with different solutions until finding one that works.
- Brainstorming: Generating a variety of ideas in a group setting to find solutions.
- The 5 Whys: Asking “why” repeatedly to drill down to the root cause of a problem.
- SWOT Analysis: Identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a situation.
- Mind Mapping: Visually organizing information to better understand and solve problems.
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa): Visualizing the causes of a specific problem to identify its root causes.
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing facts to form a judgment.
- Design Thinking: Solving problems creatively and pragmatically, focusing on the needs of the user.
- Lateral Thinking: Approaching problems in innovative and indirect ways.
- Pareto Analysis (80/20 Rule): Focusing on the most effective changes to make.
- Positive Deviance: Identifying and learning from outliers who succeed against the odds.
- Appreciative Inquiry: Focusing on what works well and how to do more of it.
- Force Field Analysis: Analyzing the forces for and against a change.
- Gap Analysis: Identifying the gap between the current situation and desired future.
- Simple Root-Cause Analysis: Investigating the primary cause of a problem.
- Affinity Diagramming: Organizing ideas or data into groups based on natural relationships.
- Flowcharting: Visualizing a process to understand and improve it.
- Checklists: Ensuring that all necessary steps in a process are completed.
- Six Thinking Hats: Using different perspectives to explore and solve problems.